While the momentum for growth has lost steam in some countries – Germany, France and Japan in particular – GDP in the United States is continuing to rise at a steady pace. Growth could even pick up pace in the course of the year as a highly expansionary fiscal policy is implemented. In 2018 and 2019, the fiscal stimulus approved by the Trump administration – in December 2017 for the revenue component, and in February 2018 for the expenditure side – would amount to 2.9 GDP points. This level of fiscal impulse would come close to that implemented by Obama for 2008. However, Trump’s choice has been made in a very different context, since the unemployment rate in the United States fell back below the 4% mark in April 2018, whereas it was accelerating 10 years ago, peaking at 9.9% in 2009. The US economy should benefit from the stimulus, but at the cost of accumulating additional debt.
Donald Trump had made fiscal shock one of the central elements of his presidential campaign. Work was begun in this direction at the beginning of his mandate, and came to fruition in December 2017 with the passing of a major tax reform, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act [1], which provided for a reduction in household income tax – in particular by reducing the maximum marginal income tax rate – and corporation tax, whose effective rate would fall from 21% to 9% by 2018 [2]. In addition to this initial stimulus, expenditure will also rise in accordance with the agreement reached with the Democrats in February 2018, which should lead to raising federal spending by USD 320 billion (1.7 GDP points) over two years. These choices will push up domestic demand through boosting household disposable income and corporate profitability, which should stimulate consumption and investment. The multiplier effect – which measures the impact on GDP of a one dollar increase in public spending or a one dollar cut in taxes – will nevertheless be relatively small (0.5) because of the US position in the cycle.
Moreover, the public deficit will expand sharply, to reach a historically high level outside a period of crisis or war (graph). It will come to 5.8% of GDP in 2018 and 7.0% in 2019, while the growth gap will become positive [3]. While the risk of overheating seems limited in the short term, the fact remains that the fiscal strategy being implemented could push the Federal Reserve to tighten monetary policy more quickly. However, an excessive rise in interest rates in a context of high public debt would provoke a snowball effect. Above all, by choosing to re-launch the economy in a favourable environment, the government risks being forced to make adjustments later when the economic situation deteriorates. This pro-cyclical stance in fiscal policy risks amplifying the cycle by accelerating growth today while taking the risk of accentuating a future slowdown. With a deficit of 7% in 2019, fiscal policy’s manoeuvring room will actually shrink.
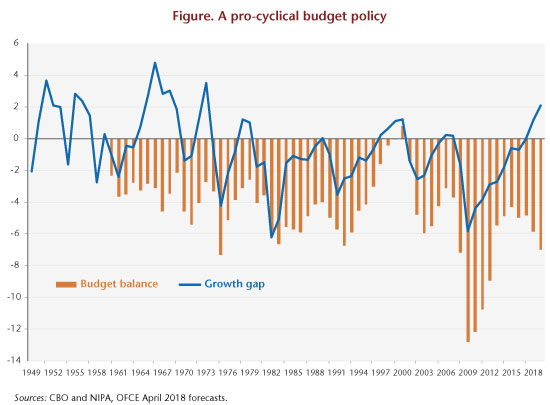
[1] See the section on Budget policy: Crisis-free acceleration [“Politiques budgétaires : accélération sans crise”] in our April 2017 forecast for greater detail.
[2] See here for more on this.
[3] The growth gap expresses – as a % of potential GDP – the difference between observed GDP and potential GDP. Recall that potential GDP is not observed but estimated. The method of calculation used by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) is explained here.
Leave a Reply