By Odile Chagny, IRES, Sabine Le Bayon, Catherine Mathieu, Henri Sterdyniak, OFCE
Most developed countries now have a minimum wage, including 22 of the 28 EU countries. France has long stood out for its relatively high minimum wage, the SMIC. But in 1999, the United Kingdom introduced a minimum wage, and the British government’s goal is to raise this level to 60% of the median wage by 2020, which would bring it to the level of France’s SMIC and among the highest-ranking countries in the OECD. More recently, in 2015, Germany also introduced a minimum wage.
Note that gross pay is a legal concept. What matters from an economic point of view is the cost of labour for a firm as well as the disposable income (including benefits and taxes) of a household in which employees earn the minimum wage.
In OFCE Policy Brief no. 34 we present a comparison of the minimum wages in force in 2017 in these three countries, using standard cases, from the viewpoint first of the cost of labour and then with respect to employees’ standard of living.
It appears that the cost of labour is slightly higher in Germany than in France, and much more so than in the United Kingdom, and that the reforms announced in France for 2019 (reducing contributions) will strengthen France’s competitive advantage vis-à-vis Germany. The cost of labour at the minimum wage is therefore not particularly high in France (Table).
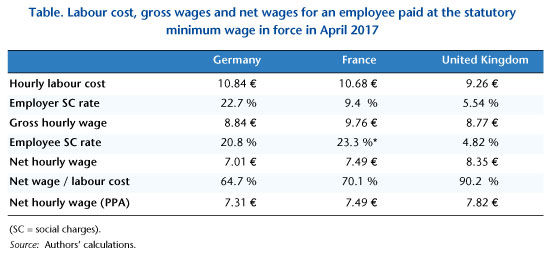
With regard to disposable income, a comparison of different arrangements for working time and family situations highlights different logics in the three countries. In Germany, the underlying rationale is to protect families from poverty, regardless of the parents’ working situation. In France, in contrast, a family with two children has to have two people working full-time at the SMIC to escape poverty, as the tax-benefit system seeks to encourage women’s integration into the labour market. France is thus the only one of the three countries where a mono-active family with two children, one of whose parents works full-time at the minimum wage, falls below the monetary poverty line (Figure).
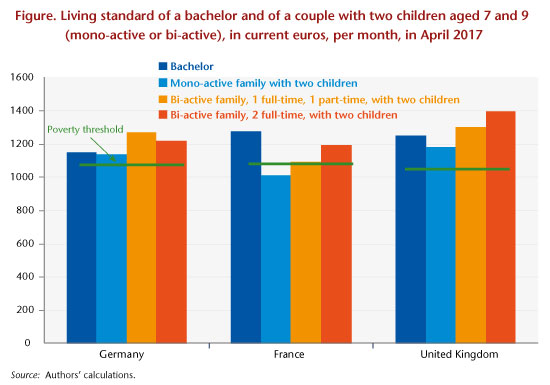 From the point of view of the relative position of minimum wage earners in relation to the general population, our study highlights the rather favourable situation of the United Kingdom. The living standard there is comparatively high: all the families considered in our typical cases have a standard of living above the poverty line, on the order of 30% higher for a family where both parents work full-time at the minimum wage. The gain from taking up a job is, as in France, high, while it is low in Germany in all the configurations.
From the point of view of the relative position of minimum wage earners in relation to the general population, our study highlights the rather favourable situation of the United Kingdom. The living standard there is comparatively high: all the families considered in our typical cases have a standard of living above the poverty line, on the order of 30% higher for a family where both parents work full-time at the minimum wage. The gain from taking up a job is, as in France, high, while it is low in Germany in all the configurations.
Finally, our analysis is contributing to the debate about the establishment of a Europe-wide minimum wage. A policy to harmonize the minimum wage in Europe, as this is conceived by the European Federation of Trade Unions and supported by France, cannot be thought of solely in terms of labour income, but also needs to take into account the goals targeted in terms of living standards, especially for families.
Leave a Reply