By Céline Antonin, Christophe Blot and Danielle Schweisguth
This text summarizes the OFCE’s October 2012 forecasts for the economy of the euro zone.
After more than two years of crisis in the euro zone, this time the meeting of the European Council, held on 18 and 19 October, had nothing of the atmosphere of yet another last-chance summit. Even though discussions on the future banking union [1] were a source of tension between France and Germany, there was no sword of Damocles hanging over the heads of the European heads of state. However, it would be premature to assume that the crisis is coming to an end. It is sufficient to recall that the GDP of the euro zone has still not regained its pre-crisis level, and in fact declined again by 0.2% in the second quarter of 2012. This decline is forecast to continue, as we expect GDP to fall by 0.5% in 2012 and by 0.1% in 2013. Consequently, the unemployment rate in the euro zone, which has already surpassed its previous historical record from April 1997, will rise further, reaching 12.1% by end 2013. What then are the reasons for the lull? Can the euro zone quickly resume its growth and hope to finally put an end to the social crisis?
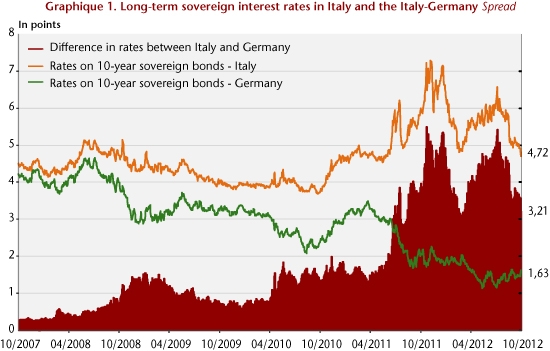
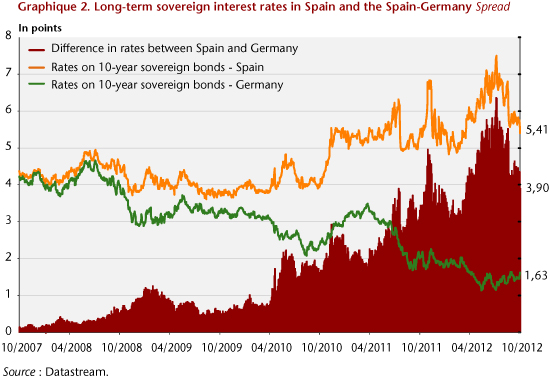
Since the end of 2011, Europe has adopted a new treaty (the Treaty on stability, coordination and governance, the TSCG) which is being ratified in the 25 signatory countries. The new law is specifically intended to strengthen both budgetary discipline — through the adoption of national golden rules — and solidarity through the creation of the European Stability Mechanism (ESM), in so far as the use of the ESM is conditional on ratification of the TSCG. On 6 September, the ECB unveiled the basic points of its new conditional purchase of sovereign debt (see here), which is aimed at reducing the interest rates of countries subject to the ESM. Thus, the risk premium, as measured by the difference between the Italian and Spanish sovereign interest rates and the German rate, after peaking on 24 July 2012, decreased respectively by 2.2 and 2.5 points (Figures 1 and 2). This is of course still far from normal, but this lull is nevertheless welcome and it shows that the spectre of a breakup of the euro zone has receded.
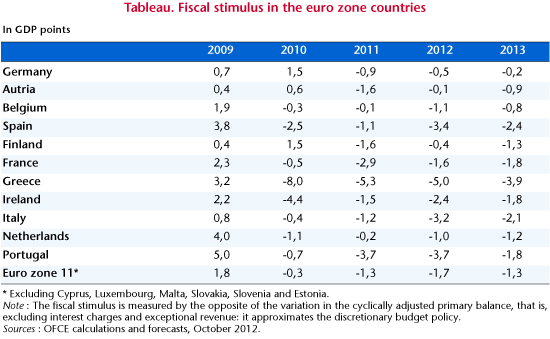
Could this new wave of optimism be a precursor to an upturn in the economy of the euro zone? The answer to this question is, unfortunately, negative. The fiscal policies of countries in the zone are still highly restrictive, a situation that has even intensified in 2012, pushing Italy and Spain back into recession and deepening the recession that was already hitting Portugal and Greece. For the euro zone as a whole, the fiscal stimulus will come to 1.7 percent of GDP in 2012 (table). The series of votes on national budgets confirms this strategy of a forced reduction of budget deficits for 2013, with the overall fiscal consolidation for the euro zone as a whole coming to 1.3%. There will be significant differences between the countries, since in Germany the fiscal stimulus will barely be negative (-0.2 point) while in Spain, Italy and Greece it will be more than -2 GDP points. However, the recessionary impact of this synchronized fiscal consolidation will be even greater given that the euro zone countries are still at the bottom of the economic cycle. In these conditions, the targets for budget deficit reduction will not be met, which will inevitably raise the question of the appropriateness of further budget cuts. More and more Member States thus risk being caught in a vicious circle where low growth calls for further fiscal adjustments that in turn deepen the economic and social crisis. It is essential that any decision about improving the governance of the European Union or the transmission of monetary policy restores confidence and creates the conditions for a return to growth. But this will be insufficient to escape the recession and should not obscure the impact of the fiscal strategy.
tab
_______________________________________
[1] See here for an analysis of the importance of the proposed banking union and the questions it raises.