By the Department of Analysis and Forecasting, headed by X. Timbeau
This article summarizes OFCE note no.16 that gives the outlook on the global economy for 2012-2013.
The sovereign debt crisis has passed its peak. Greece’s public debt has been restructured and, at the cost of a default, will fall from 160% of GDP to 120%. This restructuring has permitted the release of financial support from the Troika to Greece, which for the time being solves the problem of financing the renewal of the country’s public debt. The contagion that hit most euro zone countries, and which was reflected in higher sovereign rates, has been stopped. Tension has eased considerably since the beginning of 2012, and the risk that the euro zone will break up has been greatly reduced, at least in the short term. Nevertheless, the process of the Great Recession that began in 2008 being transformed into a very Great Recession has not been interrupted by the temporary relief of the Greek crisis.
First, the global economy, and especially the euro zone, remains a high-risk zone where a systemic crisis is looming once again. Second, the strategy adopted by Europe, namely the rapid reduction of public debt (which involves cutting public deficits and maintaining them below the level needed to stabilize debt), is jeopardizing the stated objective. However, since the credibility of this strategy is perceived, rightly or wrongly, as a necessary step in the euro zone to reassure the financial markets and make it possible to finance the public debt at acceptable rates (between 10% and 20% of this debt is refinanced each year), the difficulty of reaching the goal is demanding ever greater rigor. The euro zone seems to be pursuing a strategy for which it does not hold the reins, which can only fuel speculation and uncertainty.
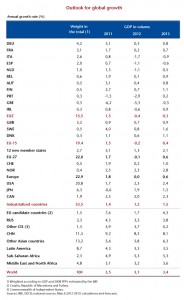
Our forecast for the euro zone points to a recession of 0.4 percentage point in 2012 and growth of 0.3 point in 2013 (Table 1). GDP per capita in the euro zone should decline in 2012 and stabilize in 2013. The UK will escape recession in 2012, but in 2012 and 2013 annual GDP growth will remain below 1%. In the US, GDP growth will accelerate from 1.7% per year in 2011 to 2.3% in 2012. Although this growth rate is higher than in the euro zone, it is barely enough to trigger an increase in GDP per capita and will not lead to any significant fall in unemployment.
The epicenter of the crisis is thus shifting to the Old Continent and undermining the recovery in the developed countries. The United States and United Kingdom, which are faced even more than the euro zone with deteriorating fiscal positions, and thus mounting debt, are worried about the sustainability of their public debts. But because growth is just as important for the stability of the debt, the budget cuts in the euro zone that are weighing on their activity are only adding to difficulties of the US and UK.
By emphasizing the rapid reduction of deficits and public debt, euro zone policymakers are showing that they are anticipating a worst case scenario for the future. Relying on so-called market discipline to rein in countries whose public finances have deteriorated only aggravates the problem of sustainability by pushing interest rates up. Through the interplay of the fiscal multiplier, which is always underestimated in the development of strategies and forecasts, fiscal adjustment policies are leading to a reduction in activity, which validates the resignation to a worse “new normal”. Ultimately, this is simply a self-fulfilling process.