The 2008 crisis almost endangered the entire global financial system. Thanks to support from governments and central banks, the banking sector has recovered and once again appears to be solid financially. In the aftermath of the crisis, the public finances of the Southern euro zone countries – Portugal, Italy, Spain and Greece – and Ireland (the “PIIGS”) have, in turn, been severely weakened. Greece was forced to suspend payments, and the risk of default is still hanging over the others. Since early 2011, bank liabilities in these economies have become a significant concern of the financial markets. Despite good stress tests, this fear intensified in August 2011. European banks then entered a new period of turmoil, and the European Central Bank was forced to lend them more than 1,000 billion euros for 3 years at a rate of 1% in order to avoid a major credit crunch.
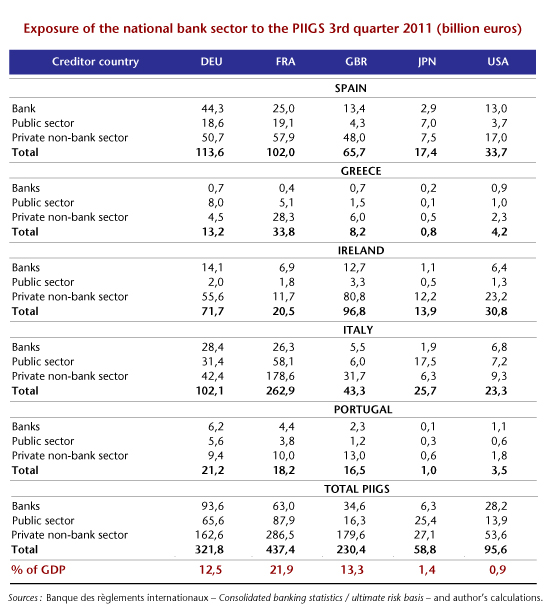
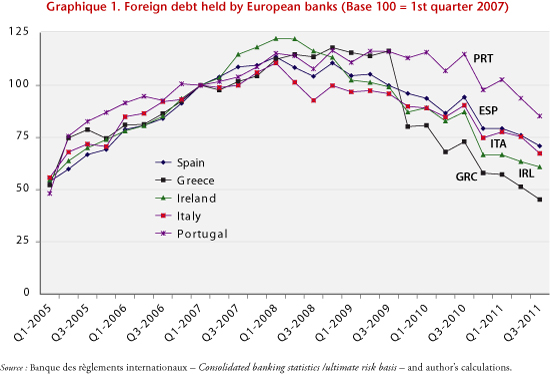
As part of their investments abroad and through their foreign branches, Europe’s banks hold liabilities from the PIIGS countries through lending to the banking sector, to the public sector (sovereign debts and credits) and to households and private non-bank enterprises. France is one of the countries that is most heavily exposed to the PIIGS (public and private sectors combined), with a total commitment by the banking system in the third quarter of 2011 of about 437 billion euros (see table), or 21.9% of GDP. Germany’s exposure, at about 322 billion euros (12.5% of GDP), is smaller. The exposure of the UK banking system is comparable and is valued at 230 billion euros, or 13.3% of GDP. In comparison, the Japanese and US banks hold little debt: 59 billion euros (1.4% of GDP) for Japan and 96 billion (0.9% of GDP) for the United States. In the course of the financial crisis, Europe’s banks have pulled back from these countries (1). According to the statistics of the Bank for International Settlements (Figure 1), the reduction in exposure was most pronounced in Greece (-55% since Q1 2007) and lowest in Portugal (-15%). Divestments of the debt of Spain (-29%), Italy (-33%) and Ireland (39%) have been comparable and are at an intermediate level compared to the previous two.
Guarantee funds can be drawn on if a bank goes bankrupt, but generally their provisions are insufficient to support a “big” bank in difficulty. According to the principle of “too big to fail”, the state must intervene to avoid bankruptcy. Possible avenues of action include acquiring some of the bank’s capital, nationalizing it by refloating it, or facilitating its long-term refinancing through the purchase of bonds. A bank failure has to be avoided at all costs, because it is frequently accompanied by panic, with collateral damage that is difficult to predict or contain. The mere fact that a State announces credible support for a bank or a banking system is often sufficient to avert a panic. If the States were to come to the rescue of the banks in the case of the Greek default, the macroeconomic implications of a 50% default on all private and public debts seem relatively minor, since it would require, for example in the case of France, a cost of around 17 billion euros, an amount that is much less than 1% of GDP (see table). By contrast, a 50% default of all the PIIGS would require 220 billion euros in support from France (11% of French GDP). The macroeconomic cost beforehand might seem high, but it is not insurmountable. Unfortunately, the spontaneous failure of one or more PIIGS would lead to an uncontrollable chain reaction whose overall macroeconomic costs could be considerable.
This financial crisis is also hitting the life insurance companies, right in the midst of a period of reform in prudential regulations. The banking sector has just managed to come up to Basel II standards and will steadily have (until 2019) to adopt Basel III (2), while the insurance industry is changing rapidly towards Solvency II (3). These two regulatory reforms are leading to an increasing need for capital just as the financial crisis is undermining balance sheets and putting greater pressure on capital ratios. While equity capital can be used to withstand a financial crisis, at the same time regulations can compel recapitalizations in very difficult refinancing conditions. This is an undesirable pro-cyclical result of the prudential regulations.
The risk of a default on payments by some PIIGS has made financial analysts pay particularly close attention to the solvency and profitability of European banks. However, the results of the stress tests (4) on the European banks published in mid-July 2011 were considered good. The hypotheses used are far from being optimistic. In the euro zone (and respectively in the other countries), they point to a fall in the growth rate of 2 points (2.4 points respectively) in 2011 and 2 points (1.9 points respectively) in 2012 compared to a reference scenario. In the euro zone, this entry into recession (-0.5% in 2011 and -0.2% in 2012) would be accompanied by higher unemployment (0.3 point in 2011 and 1.2 points in 2012), a lower inflation rate (-0.5 point in 2011 and -1.1 points in 2012), a sharp drop in property prices, a rise in long-term rates as well as discounts on sovereign debt (5) of up to 30%. The objective of this “stressed” scenario is to test the capacity of the banks to be able to maintain a “core Tier 1” ratio greater than 5% (6). Under these extreme assumptions, only 8.9% of the 90 banks tested achieved a ratio that was below the 5% ceiling that would trigger a de facto recapitalization to meet the target (7). The four French banks succeeded on the stress tests without difficulty, as they maintain high ratios: 6.6% for Societe Generale, 6.8% for the Banque populaire-Caisse d’épargne, 7.9% for BNP Paribas and 8.5% for Crédit Agricole. The countries where failures were observed include Austria (1 bank), Spain (5 failures) and Greece (2 failures). In view of the stress tests, the European banking system could therefore be considered as capable of withstanding a major economic crisis.
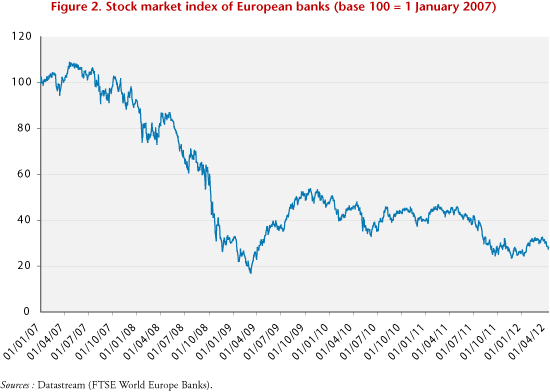
After the second aid package to Greece on 21 July 2011, and with ongoing pressure on the other sovereign debts, worry seized the stock markets, and European bank stocks fell sharply from August to December 2011 (Figure 2). These stock market changes were in complete contradiction with the positive results of the stress tests. There are three possible ways to interpret the reaction of the financial markets:
– An actual crisis would be much sharper than the hypotheses of the stress tests;
– The stress test methods are not adequate for estimating the consequences of a crisis;
– The markets get swept up in the slightest rumors and are disconnected from basics.
For now, with respect to the most pessimistic forecasts, it does not seem that the stress test hypotheses are particularly favorable. However, they have weaknesses for assessing systemic financial crisis, in that each bank does not include in its assessment the damage brought about by the application of the scenario to other banks or the consequences for the credit market. There is no feedback from the financial interconnections. Moreover, the economic crisis can greatly increase the default rates of private companies. This point may have been underestimated by the stress tests. Note also that the tests are performed at an internal level, which can also lead to different assessments of the consequences of certain scenarios. In addition, the stress tests evaluate the financial soundness of the banks, but de facto, a bank, although solvent, can see its stock price fall in times of crisis for the simple reason that its expected profitability decreases. Most importantly, the runaway financial markets are due to the lack of a consensus on the decisions taken within the European Union on finding a definitive solution to the debt crisis but also to the fact that the statutes of the European Central Bank prohibit it from participating in public debt issues. These uncertainties reinforce the volatility of the stock price of banks that are particularly exposed to PIIGS, as evidenced by the strong correlation between CDS on private banks and on sovereign debt in the euro zone (8).
With the beginning of a solution on Greek debt, the stock market listings of European banks have been rising since January 2012. Hopefully the agreement of 21 February 2012 on Greek sovereign debt will calm the storm that hit the bond markets. The operation provides that private investors agree to give up 107 billion euros of the 206 billion of debt they hold and that the euro zone States agree a new loan of 130 billion. The agreement is a swap of debt. The old bonds are exchanged against new ones at a discount of 53.5% of the face value (9) and at a new contractual interest rate. The write-down was not a surprise for the banks, which have already set aside provisions for the losses. The operation was a clear success (10), as 83% of the holdings were voluntarily offered for exchange on 9 March (11). The level of participation was increased to more than 95% by carrying through a compulsory exchange with creditors who had not responded positively to the operation (collective action clauses for debt held under Greek law). After this exchange, the European states, the IMF, and the ECB will hold “more than three-quarters of Greek debt” (12), which means that any new crisis of Greek sovereign debt would have little impact on private investors. A new source of uncertainty comes from the CDS that were taken out for the purpose of hedging or speculation (“naked CDS”). Initially, the International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) (13) announced on 1 March that this exchange was not a “credit event”. On 9 March, it revised its judgment (14). The ISDA now believes that the collective action clauses are forcing owners to accept the exchange, which constitutes a credit event. The Greek default on payments is a legally recognized event, and the CDS are thus activated. According to the ISDA, the net exposure of CDS to Greece would amount to only 3.2 billion dollars. To estimate the overall cost of the CDS for the financial sector, the residual value of the bonds would have to be subtracted from that amount. Given the inability of Greece to resume growth, the sustainability of its remaining debt is not guaranteed, and the risk of contagion persists. In any event, the public debt of the Southern euro zone countries and Ireland are now considered risky assets, which is a factor that is weakening the European banking sector. In this respect, since late March the recent rise in interest rates on Italian and Spanish public debt has provoked a decline in the stock prices of European banks (Figure 2).
The ongoing financial crisis is weakening the banking sector in the euro zone, which could lead it to reduce its exposure to risk: a major credit crunch is thus to be feared. The latest ECB survey covering 9 December 2011 to 9 January 2012 (15) with regard to the lending conditions set by banks is not very reassuring. Tighter conditions are expected by 35% (against 16% last quarter) of banks on business loans and by 29% (against 18% last quarter) of banks on consumer loans. In light of this prospect, on 21 December 2011 the ECB conducted a long-term refinancing operation. This was a huge success, with 489 billion euros in credits granted to the banking sector. The funds were loaned at 1% for a period of 3 years. Although it is still difficult to assess the impact of this measure, ECB president Mario Draghi said in February that this injection of liquidity had clearly avoided a major credit crunch. On 29 February 2012, the ECB launched a second long-term refinancing plan (16). The subscription was very substantial, with 530 billion euros disbursed. It is therefore reasonable to think that a credit crunch will be avoided.
In conclusion, the banking sector’s escape from the zone of turbulence depends on four key factors:
1) Only a long-term return to growth across the euro zone as a whole will make it possible to consolidate the public purse and reduce the number of business failures (17), thereby de facto reducing banks’ exposure to the risk of default, with responsibility incumbent on the European governments and the ECB to identify and implement the “right” policy mix and the appropriate structural measures.
2) The Greek State is insolvent; this failure in public finances must not be allowed to spread to other economies, since the banking crisis is also a test of the strength of financial solidarity in the euro zone, and it remains to be seen whether the Germans are more inclined to support Spain or Italy in case of a risk of default than they were with Greece.
3) The banking crisis has brought to the fore the procyclical effects of the prudential regulations, which need to be corrected.
4) The maneuvering room of governments as first responders in a crisis has become very limited due to their massive debt. If there is a new major shock, the ECB could have no other choice but to be the lender of last resort.
__________
[1] Note that a financial depreciation (capital loss) on the balance sheet value of assets in the PIIGS implies an automatic reduction in the exposure to these economies.
[2] http://www.bis.org/speeches/sp100921_fr.pdf
[3] http://ec.europa.eu/internal_market/insurance/solvency/background_fr.htm.
[4] European Banking Authority, 2011, http://stress-test.eba.europa.eu/pdf/EBA_ST_2011_Summary_Report_v6.pdf.
[5] European Banking Authority (2011), Methodogical Note – Additional guidance, June 2011.
[6] The minimum level required by Basel II for the Core Tier 1 ratio is only 2%, which rises to 4.5% under Basel III (in force in 2013). This ratio measures the proportion of risk-weighted assets covered by equity capital.
[7] For a bank whose ratio falls to x%, the recapitalization requirement corresponds to (5%-x)/x % of post-shock equity capital. Hence if x=4%, the recapitalization requirement would correspond to 25% of the equity capital.
[8] “The correlation between interest rates on public debt and on private debt will make it difficult to resolve the sovereign debt crisis in the euro zone”, Flash marchés, Natixis, 14 March 2011 – N° 195, http://cib.natixis.com/flushdoc.aspx?id=57160.
[9] For example, each old bond with a face value of 100 euros is exchanged for a new one worth 46.5 euros. The EFSF guarantees 15 euros and the Greek state 31.5 euros.
[10] http://www.minfin.gr/portal/en/resource/contentObject/id/baba4f3e-da88-491c-9c61-ce1fd030edf6.
[11] In light of the holders of public debt who are not subject to Greek law and who are refusing to take part in the operation, the deadline of 9 March (see http://fr.reuters.com/article/frEuroRpt/idFRL6E8F54OO20120405) was put off to 4 April and then to 20 April. The Greek state considers that this refusal to exchange will not be sufficient to block the operation, as, given the collective action clauses, voluntary or required participation amounts to at least 95.7%. With regard to the recalcitrant investors, the Greek state has the choice of waiting a little longer, meeting its contractual commitments (continued reimbursement of the face value and interest as initially scheduled), make a new exchange offer (but this must be equitable with respect to those who accepted the previous offer) or default, with the risk of pursuit in the international courts.
[12] Olivier Garnier, “Comprendre l’échange de dette publique grecque”, Le Webzine de l’actionnaire – Analyses, Société Générale, 13 March 2012, http://www.societegenerale.com/actiorama/comprendre-l%E2%80%99echange-de-dette-publique-grecque.
[13] http://www.isda.org/dc/docs/EMEA_Determinations_Committee_Decision_01032012Q2.pdf.
[14] http://www2.isda.org/greek-sovereign-cds/
[15] The Euro Area Bank Lending Survey, 1February 2012, http://www.ecb.int/stats/pdf/blssurvey_201201.pdf.
[16] http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/date/2011/html/pr111208_1.en.html.
[17] “Les entreprises après la crise”, Colloquium Banque de France, 28 June 2011, http://www.banque-france.fr/fileadmin/user_upload/banque_de_france/publications/Bulletin-de%20la-Banque-de-France/Bulletin-de-la-Banque-de-France-etude-185-2.pdf