By the OFCE France team
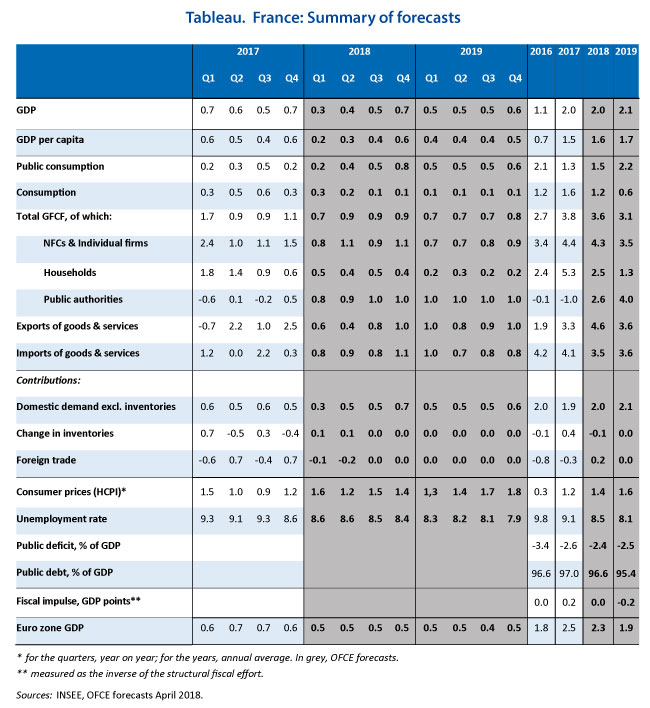
On Friday, April 27, the INSEE published the national accounts for the first quarter of 2018. With growth of 0.3%, the French economy seems to be slowing down, even though after five years of sluggish growth (0.8% on average over the period 2012-16) a recovery finally materialized in 2017 when GDP rose 2%. While the quarterly profile of GDP growth in 2018 will be marked by the timing of fiscal measures, which will affect purchasing power (rise in indirect taxation and the CSG tax) and thus the trajectory of household consumption, the impact, which is anticipated in our spring forecast (Table), should be only provisional. Household purchasing power should increase in the following quarters, with a sharp acceleration at the end of the year driven by the fall in the housing tax and the second tranche of reductions in social security contributions.
The increase in consumption, weak in the first half and strong in the second, will therefore lead growth to pick up pace through the year, from 0.3% in the first quarter to 0.7% by year end. In 2019, as a result of the rise in the tax measures to shore up household purchasing power, the latter will increase by 2.4% (from 1.6% in 2018), boosting consumption for the year as a whole (2.2% in 2019 after 1.5% in 2018), despite a further rise in indirect taxation.
Business investment is expected to continue its robust growth in 2018 and 2019, supported by the ongoing improvement in profit rates, the continued low cost of capital, and growing demand, which is keeping the utilization rate at a high level. After shrinking for several years, general government investment is set to rise again in 2018 and 2019, with the gradual roll-out of the Grand Plan d’Investissement [Major Investment Plan] and the goal of maintaining investment by local authorities. Household investment should slow, as indicated by the downturn in housing demand surveys and the outlook for housing starts, probably in connection with the reduction in budget allocations for housing and with the wait-and-see attitude on the construction market following the discussion to be expected about the ELAN bill.
A pick-up in exports, confirmed by favorable survey trends, record levels of exporter margins and strong productive investment will translate into strengthening export market shares. Given the dynamic economic environment in the euro zone, foreign trade will no longer be a drag on France’s growth in 2018 and 2019.
Given this robust growth in 2018 and 2019, job creation, driven by the market sector, will remain dynamic (+194,000 in 2018 and +254,000 in 2019), which will push down the unemployment rate to 8.4% by the end of 2018 and to 7.9% by the end of 2019 (compared to 8.6% in the fourth quarter of 2017). On the other hand, the sharp fall in new government-assisted contracts in 2018 will slow the pace of the reduction in unemployment, despite the ramp-up of the Plan Formation et de la Garantie jeunes (Training Plan and Youth Guarantee).
The public deficit will be reduced only slowly (2.4% of GDP in 2018 and 2.5% in 2019, after 2.6% in 2017), but this masks a sharp improvement in the government balance, which will reach 1.6% in 2019 excluding the one-off measure related to the conversion of the CICE credit into reductions in social contributions. However, deficit reduction should be sufficient to ensure that France leaves the corrective arm of the Stability Pact and to begin to reduce the public debt (from 97% of GDP in 2017 to 95.4% in 2019).
Leave a Reply